Political system
Present day Benin was the site of Dahomey, a West African kingdom that rose to prominence in about 1600 and over the next two and a half centuries became a regional power, largely based on its slave trade. Coastal areas of Dahomey began to be controlled by the French in the second half of the 19th century; the entire kingdom was conquered by 1894. French Dahomey achieved independence in 1960; it changed its name to the Republic of Benin in 1975.
The President is directly elected by absolute majority popular vote in 2 rounds if needed for a 5-year term (eligible for a second term); last held on 6 March and 20 March 2016 (next to be held in 2021). The National Assemble (Assemblee Nationale) is formed of 83 seats; members directly elected in multi-seat constituencies by proportional representation vote; members serve 4-year terms.
- Area : 11.622 km2
- Population : 11.340.504 (July 2018)
- Density : 70.4 people/km2
- Population growth rate : 2.98%
- Urban population : 47.3% (2018)
- Official language : French
International agreements
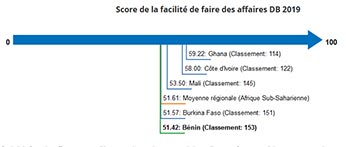
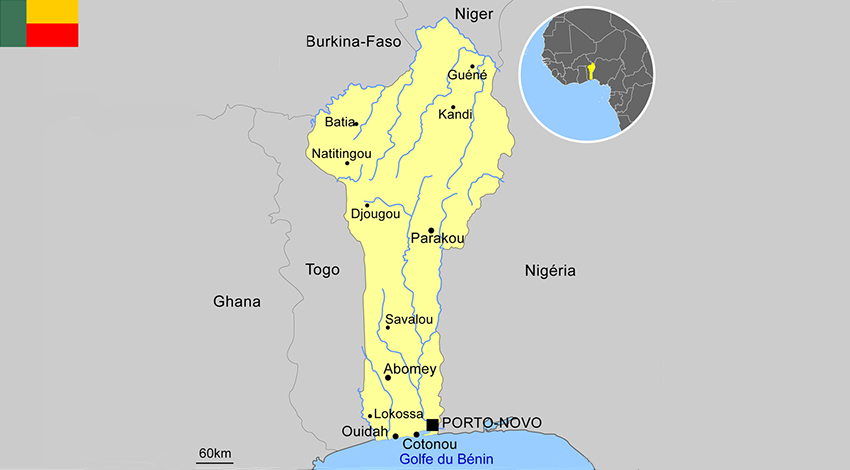
- Benin (capital : Porto-Novo)
- Burkina Faso (capital : Ouagadougou)
- Cape Verde (capital : Praia)
- Ivory Cost (capital : Abidjan)
- Gambia (capital : Banjul)
- Ghana (capital : Accra)
- Guinea (capital : Conakry)
- Guinea Bissau (capital : Bissau)
- Liberia (capital : Monrovia)
- Mali (capital : Bamako)
- Niger (capital : Niamey)
- Nigeria (capital : Abuja)
- Senegal (capital : Dakar)
- Sierra Leone (capital : Freetown)
- Togo (capital : Lomé)